PROTECTING PUPPIES FROM PARVOVIRUS

VMBS NEWS — March 28, 2024

Springtime brings a vibrant burst of life and marks a time when many puppies are born.
As a result, the spring also presents peaks in canine health concerns that can impact puppies in the months after they are born. Among these is parvovirus, a highly contagious and potentially deadly disease.
Dr. Kathleen Aicher, an assistant professor at the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, explains why parvovirus is so contagious between dogs, emphasizing the vulnerability of puppies and how crucial vaccinations and treatment are in preventing the infection from spreading.
The Role Of Parvo Vaccinations
There are several factors that make parvovirus a highly contagious infection that can be fatal without prompt and intensive veterinary care.
“Parvovirus is very easily transmitted between dogs because it takes very little exposure to cause infection, and dogs who are infected can shed the virus for a few days before they exhibit symptoms, unknowingly exposing other dogs to the virus,” Aicher said. “The virus is also very resistant to extreme temperatures and cleaning, so it can remain in the environment for a long time, putting dogs at further risk.”
Parvovirus is especially dangerous for puppies, who have weaker immune systems compared to adult dogs and are highly susceptible to parvo until they are fully vaccinated.
In fact, most puppies and dogs that get sick with parvovirus either have not been vaccinated or have not yet completed their vaccination schedule.
“Puppies may get some initial parvovirus protection by antibodies from the mother, if she is vaccinated, but it is unknown how long this protection might last,” Aicher explained. “For these reasons, there are well-established vaccine schedule guidelines that veterinarians follow to keep puppies protected during the time that they are most vulnerable to infection.”
Vaccinations against parvovirus — which have significantly reduced the number of infected dogs — should initially be given by veterinarians when puppies are 6-8 weeks old, followed by boosters up to 16-20 weeks old.
Until they are fully vaccinated, Aicher encourages owners to keep their puppies away from areas where dogs congregate, such as dog parks, doggy day care, boarding facilities, and pet stores, particularly if they are displaying any signs of illness.
“If owners want to begin training their puppy in a class with other owners and puppies, they may be able to find places in which there is a policy of only allowing healthy, vaccinated puppies and that practice effective and regular disinfection of the facility,” Aicher said. “Owners might also bring their puppy to spend time with fully vaccinated, healthy adult dogs who belong to friends or family members.”
Battling Parvo With Veterinary Care
Despite the effectiveness of vaccines, owners should remain aware of parvovirus symptoms, as early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in recovery for puppies.
“Parvovirus is always suspected highly for any suddenly sick puppy, regardless of vaccination history, and any such puppy should see their veterinarian right away,” Aicher said. “Classic symptoms of parvovirus include severe diarrhea, particularly with blood or a very bad smell. Puppies may also be vomiting, have a poor appetite, feel warm or very cool to the touch, or act lethargic and weak, with very low energy.”
Because of how infectious parvovirus is, Aicher advises owners to contact their veterinarian before bringing in a sick puppy for an appointment, allowing the veterinarian’s office to take precautions that protect both the puppy and other dogs in the hospital.
“Many veterinary hospitals will treat any sick puppy as a parvovirus suspect until proven otherwise, which means they might wear protective gear, use a special exam room, or want to test your puppy for parvo before bringing them into the hospital,” Aicher explained. “The typical test for parvovirus is very easy to perform and results can be obtained very quickly.”
Veterinarians will then discuss the diagnosis in more detail and share their concerns based on the puppy’s history and physical exam. Aicher noted that, frequently, infected puppies will need to remain hospitalized for supportive care until they recover because of how sick they can become.
Despite the dangers of parvovirus, the impact of the disease can be reduced with proper vaccination and swift veterinary care, ensuring that puppies grow up healthy and happy.
Pet Talk is a service of the School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University. Stories can be viewed on the web at vetmed.tamu.edu/news/pet-talk. Suggestions for future topics may be directed to vmbs-editor@tamu.edu.
Household Cleaner Puts Puppies at Risk, a Veterinary Toxicologist Says
https://www.inverse.com/science/household-cleaners-pets-safety-toxicity
Many cleaning products contain chemicals that, in large enough amounts, can be toxic to animals.
BYELANA SPIVACK MARCH 9, 2024 FROM INVERSE.COM
Cleaning products are crucial to keeping our homes clean and fresh. But are they safe for the furry creatures that live with us? Pets like cats and dogs stick their noses in so many things, not all of which are good for them. With that in mind, here’s how to ensure your cleaning routine is safe for your non-human best friend.
IT’S ALL ABOUT CONCENTRATION
Many cleaning products contain chemicals that, in large enough amounts, can be toxic to humans and animals. Senior veterinary toxicologist Ahna Brutlag at the Pet Poison Helpline and member of the American Board of Veterinary Toxicology, says bleach, ammonium, phosphoric acid, hydrogen peroxide, sodium hydroxide, and any type of phenol all appear in common household cleaners. When applied to the eyes or skin, like the exposed paw pads, they can irritate and even burn your furry friend.
But there is some good news: The concentration of these products matters, Brutlag says. Multipurpose surface and glass cleaners, for example, “have a pretty wide margin of safety,” she tells Inverse. What’s most crucial is using these products according to their directions. For example, if a spray directs you to rinse a surface with water after applying, then you certainly should.
Brutlag also suggests keeping pets away from freshly spritzed areas. A rule of thumb is that the area is safe again once you can no longer smell it. At that point, the spray has set and evaporated into the ether. Opening a window or turning on a ventilator while you’re cleaning can help to circulate fresh air for you and your pets and get rid of the smell faster.
NON-MAMMALS NEED PROTECTION, TOO
Opting for homemade cleaners made from vinegar, baking soda, and lemon isn’t necessarily safer, either. Vinegar may seem like a more wholesome option, but it will still sting your cat’s tongue if they walk through some and then groom themselves.
Brutlag calls out exotic pets. Birds are vulnerable to inhaling airborne particles that aerosols and spray bottles produce, so removing them from a room when using these chemicals is imperative. Amphibians can absorb compounds through their skin, so ensuring they’re safely locked away in their enclosures is a must. Once a cleaner’s scent disappears, feel free to uncover their tank again.
“PREVENTION, PREVENTION, AND PREVENTION”
More potent, corrosive cleaners like oven, drain, and toilet cleaners and rust removers, “have the potential to be significantly more harmful for people and pets.” These more caustic ingredients come in higher concentrations, so these products are much less diluted. “An ingredient is safe or dangerous based on the concentration,” she says.
These products also have a significantly higher or lower pH balance, which measures how acid or alkaline a substance is on a scale of 0 to 14. Water, for example, is completely neutral at 7. Bleach, oven cleaner, and drain cleaner come in at 13 and 14, making them extremely basic. These extremes make them such effective cleansers, but if you’re still concerned about their potency, you can dilute them further.
Dogs, especially puppies, are at high risk for poisoning because of their penchant for eating foreign objects. The form a cleaner comes in may also make it more dangerous to animals. According to David Dorman, professor of toxicology at North Carolina State University’s College of Veterinary Medicine, bite-sized dish and washing machine pods are of particular risk to dogs, who love putting things in their mouth. He urges pet owners not to discount any substance as a potential harm. This isn’t to say you should stop buying them, but rather that you should use and store them carefully.
Another aspect of cleaning and pet safety comes from how well-prepared you are. Dorman has three safety rules: “Prevention, prevention, and prevention,” he tells Inverse. Properly storing cleaning agents out of reach can save you and your pet a world of suffering. If that fails, then having a poison control number on the fridge means less vital time wasted looking up information.
If your pet walks through a puddle of cleaner or spills some on their coat, their skin or eyes may burn. You may notice your pet pawing at their eyes or chewing on a body part more than usual. In some cases, the strongest corrosives can even burn your pet’s tongue. Dorman suggests doing your best to wash the exposed area off with running water, though he acknowledges not every pet, especially those in discomfort, will be amenable to that.
Household cleaners are safe to keep around your pets as long as you’re mindful of where you keep them and how you use them. Provided you do that, cleaning around your pets should be a stress-free chore.
MORE LIKE THIS
Angel Fund Helps Cheeto, a Tabby, with Blocked Bladder

One day a few weeks ago, Ashley Bettencourt came home from her job as a pre-school teacher and found her tabby cat Cheeto in distress.
“He wasn’t himself,” she said. “He wasn’t eating. He was lethargic and was lying on the tile in the hallway. He wasn’t moving. Nothing worked that I knew would make him excited.
“I thought maybe he was constipated but I pressed on his belly and it was really hard. It made me nervous. So I called the Cat Care Clinic where my in-laws take their cats. After taking him in for an examination, I was told that he had a blocked bladder – he wasn’t able to urinate.”
That was on a Friday. Dr. Maggie Mills treated Cheeto. “They didn’t have to do surgery but they kept him in the hospital the whole weekend so they could keep an eye on him,” Ashley said. “They put in a catheter. But they said he took it out himself. So they put the tubes back in and he didn’t fight them again.
“When I took him in to the clinic, I wasn’t expecting what was coming,” she said. “I thought he was constipated and they would fix it and I would take him home. So when it came time to pay I was like, ‘I can’t do this.’
But the staff at Cat Care was understanding and helpful. April, the assistant practice manager, “was so sweet and nice,” Ashley said. “She printed me out a list of foundations that could help and she pointed out who to call and told me what to do. Angel Fund was the first to say, ‘We’ll help you.’ I had never done something like that before. It was overwhelming in a good way.
“I went home and I cried that night. I thought what happened was amazing. I couldn’t believe it.” She said that she found another charitable group that helped pay her bill. And the Cat Care Clinic found some money from another fund and they used that to help as well, she said.
“They said (at Cat Care) that, if we couldn’t do this, they would have had to euthanize Cheeto. He always had been such a healthy cat that is horrible to even think about. I love that Angel Fund and the veterinary association are letting people know about this. I wouldn’t have known if it wasn’t for Dr. Mills and April.”
Cheeto recovered quickly. “Now, he is good, he’s happy,” Ashley said. “He’s lost a lot of weight. But he’s eating well. He’s drinking a lot of water. And he’s fine, he’s active and he’s playing with our other cats.”
Cheeto is the father of the other cats, Roxy, Khola Man and Sprinkles – all named by Ashley’s daughters. There is also a dog in the family, Benny a miniature Doberman, with whom Cheeto is a best buddy. “We are a house that loves our fur babies,” Ashley said.
Cheeto became a member of the family after Ashley’s husband found him hiding among tires at the warehouse where he worked. He was a three-week-old kitten at the time and had to be bottle fed.
Ashley is a single parent to three daughters: Bella, 13; Skylar, 11 and Audrina, 7. She loves her job as a pre-school teacher. “It’s challenging but I love it. my students are four and five. They talk fast but they’re willing to learn and they love it.”
Angel Fund Helps Rescue Beba and Alvarado Family

A few months ago, Laura Alvarado said, her family noticed a beautiful gray cat spending time in their backyard in Long Beach.
“The cat looked scared and it was hanging around in our yard. So we decided to rescue it. It was very friendly and it came to us,” Laura said. “My mom took the cat in the house and took care of her. We had never had cats, just dogs before. We got her the shots she needed and had her spayed.”
But not long after taking in the cat they named Beba, a beautiful short-haired gray domestic, the Alvarado family got some shocking news. Beba was pregnant – and she needed to have a cesarean section. Leticia, Laura’s mother, had taken Beba to Los Coyotes Pet Hospital, where she was examined by Dr. Sonah Jo.
In early April, the surgery was performed. None of the kittens survived. “Dr. Jo told us to give Beba a lot of love because cats mourn the death of their kittens,” Laura said. “We have been giving her as much love as we can and she’s doing great.”
The Alvarado family gets by on a limited income. Leticia had to quit her job to provide care for a son, Gustavo Jr., who is disabled. Gustavo, the father, can no longer work and gets a disability check. Laura works as a probation officer in Riverside. She spends half her days there and the other half at her parents’ home.
Dr. Jo told Leticia about Angel Fund. “We couldn’t have paid for the surgery without it,” Laura said. “When Angel Fund was brought to our attention, it was just a sigh of relief. We didn’t think when we rescued Beba, that we’d have to be so involved financially.
“Angel Fund was really great. What they did for us was amazing.” The grant was for $232.49, an amount matched by the hospital. “We were devastated by what happened,” Laura said. “We didn’t know what to do.” Angel Fund helped provide the Alvarado family with the answer.
Cat-transmitted sporotrichosis: A looming threat?

ByCaitlyn Stulpin Fact checked byCarol L. DiBerardino, MLA, ELS
A potential threat on the CDC’s radar is a fungal infection being transmitted by feral cats — initially in Brazil, but now in other countries as well.

that are easily transmitted to other animals and humans.
Image: Adobe Stock
The CDC issued a warning last year about the potential threat of sporotrichosis in the U.S.
According to CDC, cats carry high loads of Sporothrix brasiliensis that are easily transmitted to other animals and humans via bites and scratches, contact with lesions, droplet exposure and inhalation.
“It’s super contagious, so you can imagine where it just took off in the feral cat population. There are hundreds of thousands of feral cats in these cities,” Tom M. Chiller, MD, MPHTM, chief of the CDC’s Mycotic Diseases Branch, told Healio, referring to the large cities in Brazil where it was first recognized. “Before you knew it, you saw this increase from 100 cases to 1,000 to hundreds of thousands of cases in cats.”
According to the CDC, sporotrichosis has spread across Brazil and other areas of South America but has not been identified in the U.S.
“A cat can shake its head and the spores can fly and land on your skin and you can become infected. That’s unheard of for these types of fungi,” Chiller said. “It’s a bit freaky that this organism has the ability now to be infectious in this other form. That concerns me.”
In 2022, researchers reported the first three cases of cat-transmitted sporotrichosis outside South America, occurring in the United Kingdom. According to the report, the first case was in an older woman with no history of recent travel to Brazil or immunosuppression who was scratched by a domestic cat. The second case occurred in the woman’s daughter, who also had no history of recent travel to Brazil but had been scratched by the same cat. The third case was in a healthy veterinarian who was scratched by the same cat during an exam at his veterinary practice.
The infections were “likely acquired from an indoor domestic cat which had previously lived in South-Eastern Brazil 3 years previously,” the authors concluded. “This suggests that S. brasiliensis can lay dormant for many years and has implications for global public health.”
The authors urged veterinarians to be vigilant in taking a travel history when seeing cats with unexplained lesions and for animal health authorities worldwide to reexamine border control policies to consider pre-import screening of cats from endemic areas.
According to Chiller, no human-to-human transmission has been documented yet.
References:
- American Veterinary Medical Association. CDC issues warning about spread of cat-transmitted sporotrichosis. https://www.avma.org/news/cdc-issues-warning-about-spread-cat-transmitted-sporotrichosis. Published March 29, 2023. Accessed Feb. 24, 2024.
- Barnacle JR, et al. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2022;doi:10.1016/j.mmcr.2022.12.004.
- CDC. Sporotrichosis. https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/sporotrichosis/index.html. Last reviewed Feb. 9, 2022. Accessed Feb. 24, 2024.
Published by:
Novel cancer vaccine offers new hope for dogs — and those who love them
A Yale researcher developed a vaccine that can slow or halt certain cancers in dogs. And it could be used to treat humans in the future.
By Mallory Locklear march 5, 2024
During a sunny morning on Florida’s Gulf Coast last month, an 11-year-old golden retriever named Hunter bounded through a pine grove. Snatching his favorite toy, a well-chewed tennis ball attached to a short rope, he rolled through the tall grass, with an energy that seemed inexhaustible. A passerby might not have even noticed that this playful golden has only three legs.
For Deana Hudgins, the dog’s owner, it seems almost unthinkable that two years ago Hunter was diagnosed with osteosarcoma, a form of bone cancer that kills upwards of 65% of the dogs it afflicts within 12 months, in his left front leg.
For many years Hunter worked alongside his owner as a search-and-rescue dog, helping find victims of building collapses and other disasters. He no longer performs those duties, but does still help Hudgins train other dogs. The energetic golden can also run, fetch, and catch as well as ever.
And two years since his initial diagnosis, Hunter has no signs of cancer. The dog’s life-saving treatment incorporated typical approaches, including amputation of the left leg and chemotherapy. But Hunter also received a novel therapy — a cancer vaccine developed by Yale’s Mark Mamula.
If we can provide some benefit, some relief — a pain-free life — that is the best outcome that we could ever have.”
The treatment, a form of immunotherapy that is currently under review by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), which regulates animal treatments, has been subject to multiple clinical trials over the past eight years. And the results are promising; for hundreds of dogs, including Hunter, the vaccine has proved effective.
Mamula, a professor of medicine (rheumatology) at Yale School of Medicine, believes the vaccine offers a badly needed weapon in the fight against canine cancer.
“Dogs, just like humans, get cancer spontaneously; they grow and metastasize and mutate, just like human cancers do,” said Mamula. “My own dog died of an inoperable cancer about 11 years ago. Dogs just like humans suffer greatly from their cancers.
“If we can provide some benefit, some relief — a pain-free life — that is the best outcome that we could ever have.”
Even as recently as a decade ago, Mamula didn’t anticipate that he would one day develop a cancer vaccine for dogs. A rheumatology researcher, he studies autoimmune diseases like lupus and Type 1 diabetes and how the body gives rise to them.
But that work eventually led him to cancer research as well.
Autoimmune diseases, Mamula says, are characterized by the immune system attacking the body’s own tissues; in the case of Type 1 diabetes, the immune system targets cells in the pancreas.
Then several years ago, using what they knew about autoimmunity, Mamula and his research team developed a potential cancer treatment that they say initiates a targeted immune response against tumors.
“In many ways tumors are like the targets of autoimmune diseases,” he said. “Cancer cells are your own tissue and are attacked by the immune system. The difference is we want the immune system to attack a tumor.”
It was a chance meeting with a veterinary oncologist soon thereafter that made Mamula think that this novel treatment might work well in dogs.
Targeting tumors

There are about 90 million dogs, living in 65 million households, in the United States alone. Around one in four dogs will get cancer. Among dogs 10 years or older, that ratio jumps to around one in two.
Yet the therapies used to treat these cancers remain fairly antiquated, Mamula says.
“There have been very few new canine cancer treatments developed in decades — it’s a field that is begging for improvement,” he said.
In 2015, Mamula met a veterinary oncologist named Gerry Post. During his 35-year career Post has treated cancer in snakes, turtles, and zoo animals. But most of his patients are dogs and cats.
Through conversations with Post, Mamula realized that it wouldn’t be difficult to make the leap from human to dog cancers. Together they would launch an early-phase study into Mamula’s dog cancer vaccine.
“Dog and human cancers are quite similar in a number of ways,” said Post, chief medical officer of One Health Company, a canine cancer treatment group, and an adjunct professor of comparative medicine at Yale School of Medicine. “Whether it’s how the cancers appear under the microscope, how the cancers behave, respond to chemotherapy, develop resistance, and metastasize.”
After talking with a veterinary oncologist, Mamula realized that it wouldn’t be difficult to make the leap from addressing human cancers to dog cancers.
Even the types of cancers that afflict dogs and humans are similar. Like humans, dogs can get melanoma, breast cancer, colon cancer, and osteosarcoma, among others.
When it comes to curing these diseases, these similarities bring an important benefit: understanding cancer in one species will help scientists understand cancer in the other. And treatments that work well for one may actually work well for both.
Several types of cancers in both humans and dogs have been found to overexpress proteins known as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). These include colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and osteosarcoma. One type of treatment currently given to human patients with these cancers involves monoclonal antibodies, proteins that can bind to and affect the function of EGFR and/or HER2. However, patients can develop a resistance to them and their effects wane over time.
For their treatment, Mamula and his team wanted to take a different approach.
Monoclonal antibody treatments are produced from one immune cell and bind to one part of the EGFR/HER2 molecules, but Mamula and his team wanted to induce a polyclonal response.
Doing so, he says, would create antibodies from multiple immune cells, rather than just one, which could bind to multiple parts of the EGFR/HER2 molecules instead of a single area. This would, in theory, reduce the likelihood of developing resistance.
The research team, led by Hester Doyle and Renelle Gee, who are both members of Mamula’s Yale lab, with assistance from the New Haven-based biotechnology company L2 Diagnostics, LLC, tested many different candidates in order to find just the right compound. They eventually found one.
After first testing it in mice, and finding promising results, they initiated their first clinical trial in dogs in 2016.

‘I was willing to try whatever I could’
Deana Hudgins knew there was something special about Hunter before she brought him home as an 8-week-old puppy, back in 2012, and began training him to be her next search-and-rescue partner.
The smallest of 18 puppies from two litters, Hunter wasn’t the obvious choice when she began looking for a partner.
“He was the runt,” said Hudgins, who has been training search-and-rescue dogs since 2001 and now runs her own company, the Center for Forensic Training and Education, which provides canine training in Ohio and Florida. “But in his case, it made him a little scrappy. He was small but very confident and very brave.
“When all of the other puppies were sleeping at the end of the day, he was still running around, climbing all of the toys, retrieving things. We need confident puppies, and that’s what he possessed.”

By the time he was a year old, Hunter began aiding searches at sites across the United States, working with local law enforcement and the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), following natural disasters. His first search, in 2014, was at the site of a mudslide in Oso, Washington that killed 43 people. In his final FEMA search, he helped search for victims of the devastating condominium collapse in the Miami suburb of Surfside, Florida, in June 2021. Hunter was involved in hundreds of searches in the years between.
In 2022, Hunter was still very active — and had just earned another service certification — when Hudgins noticed that he seemed uncharacteristically sore following a five-day training class.
“I’ve always been very proactive with my dogs because I spend every day with them, and so I notice very little things,” she said. “And he’s not a dog to limp.”
A veterinarian assumed that Hunter had strained something, suggesting anti-inflammatories, but Hudgins insisted on an x-ray. The test revealed the osteosarcoma in Hunter’s leg.
After doing a lot of research, and consulting with different veterinary groups about what steps to take, Hudgins decided that amputation offered the best chance for Hunter’s survival, along with chemotherapy.

But during that research, Hudgins had also come across Mamula’s vaccine trial. So she reached out to a colleague, James Hatch, a former Navy SEAL who trained dogs in the military and whose nonprofit supports service dogs. Hudgins knew that Hatch also happened to be at Yale, where he is a student in the Eli Whitney Students Program.
“I was willing to try whatever I could to keep [Hunter] around as long as possible,” said Hudgins. “We ask a lot of our working dogs. They work in environments that are very dangerous and often deadly. And my promise to all of them is I will do whatever I have to do to give them the best, healthiest, longest life possible. Dogs don’t survive this disease so there was no downside to me for trying the vaccine.”
Hatch connected her with Mamula, and soon Hunter was part of the clinical trial. He received his first vaccine dose ahead of his amputation surgery, his second before initiating chemotherapy, and a booster last summer.
Twenty-two months since his cancer diagnosis, Hunter is now considered a long-term osteosarcoma survivor and Hudgins says he’s thriving.
“He adjusted very well to his front limb amputation,” she said. “He continues to run around the yard. He swims in the pool. He comes with me to training and chases the other dogs around the yard.”

During a recent morning in Florida, Hunter drifted toward a nearby pond while playing outside. Hudgins, knowing the potential risks of straying too close to a pond in Florida (“There are alligators everywhere.”), quickly called him back. Hunter immediately returned to her.
“From a very young age, Hunter wanted to learn the rules of the game,” she said. “He was eager to go to work every day. I am very, very lucky to have been able to be his partner for 10 years. Hunter is one of those once-in-a-lifetime dogs.”
‘A whole new toolbox’
Hunter’s positive response to the treatment is one many other dogs have experienced as well.
To date, more than 300 dogs have been treated with the vaccine during a series of clinical trials, which are still ongoing at 10 sites in the U.S. and Canada. The findings, which have been published in a peer-reviewed study, have shown that the treatment creates antibodies that are able to home in on and bind to tumors, and then interfere with the signaling pathways responsible for tumor growth.
According to the research team, the vaccine increases the 12-month survival rates of dogs with certain cancers from about 35% to 60%. For many of the dogs, the treatment also shrinks tumors.
While future studies will determine if the vaccine can reduce the incidence of cancer in healthy dogs, the treatment for now remains a therapeutic treatment option after a cancer diagnosis has been made.
Witnessing the happiness that successful therapies provide to families with dogs is incredibly rewarding.
But even this represents something more than just “a new tool” in the fight against canine cancer, Post says. It’s a whole new toolbox.
“And in veterinary oncology, our toolbox is much smaller than that of human oncology,” he said. “This vaccine is truly revolutionary. I couldn’t be more excited to be a veterinary oncologist.”
Mamula has created a company, called TheraJan, which aims to eventually produce the vaccine. Last year, the company (whose name is inspired, in part, by the late Yale immunologist Charles Janeway, who was Mamula’s mentor) won a Faculty Innovation Award from Yale Ventures, a university initiative that supports innovation and entrepreneurship on campus and beyond.
While launching clinical tests of the vaccine’s effectiveness in humans may be a logical future step, for now Mamula is focused on getting USDA approval of the vaccine for dogs and distributed for wider use.
No matter where it goes, it’s a project close to his heart.

“I get many emails from grateful dog owners who had been told that their pets had weeks or months to live but who are now two or three years past their cancer diagnosis,” he said. “It’s a program that’s not only valuable to me as a dog lover. Witnessing the happiness that successful therapies provide to families with dogs is incredibly rewarding.”
And once the vaccine becomes available for public use, he says, for working dogs like Hunter it will always be free of charge.
media contact Fred Mamoun: fred.mamoun@yale.edu, 203-436-2643
Managed by the Office of Public Affairs & Communications
Copyright © 2024 Yale University · All rights reserved · Privacy policy · Accessibility at Yale
Ear Mites in Dogs

Not all messy ear conditions are due to mites. Learn to recognize the signs of ear mites in dogs and get appropriate treatment for your dog’s ear mite infection.
By Dr. Jennifer Bailey, DVM – Published: February 27, 2024
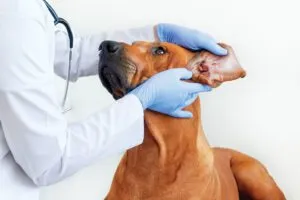
Are itchy, stinky ears interfering with your dog’s daily dose of fun? A quick internet search might lead you to ear mites in dogs as the culprit. You can try administering an ear mite medication in your dog’s ears to alleviate his discomfort. But before you reach for that over-the-counter ear mite medication, you should know more about ear mites in dogs, and learn when to call in a professional (in other words, your dog’s veterinarian!).
Otodectes cynotis is an ear mite that infects the ear canals of dogs, cats, rabbits, and ferrets. Although this species of ear mite prefers these three species of mammals, any mammalian species will satisfy its needs for survival. It survives by ingesting the dead skin cells and ceruminous exudate (ear wax) that line the ear canals.
Symptoms of ear mites in dogs

Ear mites in dogs cause an inflammatory reaction in their ear canals. This is what causes your dog to scratch at his ears and shake his head. The ceruminous glands that line your dog’s ear canals ramp up production of even more ear wax to drive out the ear mites. That smelly, dark brown, crumbly discharge in your dog’s ears is a combination of ear wax, ear mites, and their excrement. It often resembles the color and texture of coffee grounds.
Dogs who have ear mites will often develop a secondary bacterial and/or yeast infection in their ears. This can change the color and texture of the ear discharge from crumbly brown to creamy yellow or green. Sometimes the discharge may be mixed with blood if your dog scratches his ears so hard that they bleed.
If it becomes too crowded inside your dog’s ears, then some of the mites will leave the ear canals to find more spacious living quarters. Ear mites can live on the skin surface outside of your dog’s ears, snacking on skin oils and dead skin cells. They can be found crawling on the skin around the ears and on the neck and face. When your dog curls up in a ball to sleep, the mites can crawl out of the ears onto the skin of the rear end or tail. Mites will cause itchiness wherever they reside, so dogs with ear mites may scratch and develop skin redness and bald spots in areas besides their ears.
The only way to accurately diagnose an ear mite infestation is to examine a sample of your dog’s ear discharge under a microscope. The average length of an ear mite is only three-tenths of a millimeter. While this is too small to be seen by most people’s unaided eyes, ear mites can be easily spotted under a low-power microscope lens.
Treatment for ear mites in dogs
There are several treatments available to rid your dog of ear mites. But the only dogs who should receive treatment for ear mites are ones who have been diagnosed with ear mites or who live in a home with a pet who has been diagnosed with ear mites. Ear infections caused by bacteria, yeast, or a combination of bacteria and yeast can look similar to ear mite infestations.
It is important to know what you are treating before you treat. Using the incorrect treatment can worsen the underlying problem, cause more pain for your dog, and may lead to hearing loss or deafness. If your dog is scratching at his ears, shaking his head, and having discharge from his ears, have your dog examined by a veterinarian as soon as possible to determine the best course of treatment.
How do dogs get ear mites?
Ear mites spend their entire life cycle on one or more host animals. Ear mites can live for a few days in the environment but cannot survive without being on a host animal.
Ear mites spread by crawling between animals. They cannot hop or jump. To become infested with ear mites, a dog must have direct contact either with another animal who has ear mites or the gunk that recently came out of an infected animal’s ears.
How to prevent ear mites in dogs
Regularly use a flea or heartworm preventative that contains an ingredient shown to be effective against ear mites, such as Revolution, Advantage Multi, Interceptor, Nexgard, Bravecto, or Simparica.
If there are cats in the home who venture outside, regularly use a flea preventative on those cats that contains an ingredient shown to be effective against ear mites, such as Revolution, Advantage Multi, or Bravecto.
If there are ferrets in the home who venture outside on a harness and leash or rabbits in the home who spend time outdoors in a hutch or pen, talk to your veterinarian about applying Revolution monthly to these pets. This is an off-label use of Revolution in these species and must be prescribed and dosed correctly by your veterinarian.
Dr. Jennifer Bailey is a 2012 graduate of the Western University of Health Sciences College of Veterinary Medicine. She is an emergency and urgent care veterinarian at an emergency and specialty practice in Syracuse, New York.
What To Do If Your Dog Or Cat Is Stung By A Bee

Exploring new places with your pets often includes spending time outdoors. And being out in nature means you’re more likely to run into stinging insects. In this post you’ll learn what to do if your dog or cat is stung by a bee.
No one likes being stung. At the very least, it’s going to be uncomfortable. And because dogs and cats can have allergic reactions similar to humans, being stung by a bee can be a serious concern. Fortunately, there are some steps that you can take to help keep the bees at bay.
Avoid Confrontations
The safest strategy is to avoid a tangle with the wrong insect … though convincing your pets to cooperate can be difficult! So, it’s important to take some precautions to help your dog or cat stay away from bees.
Start in your yard by growing plants like chrysanthemums, lemongrass, or primrose, which don’t attract bees. When you and your pet are outside, burn citronella candles and don’t leave food outdoors. And make sure you’ve trained your dog to “leave it” whenever he’s tempted to put his nose where it doesn’t belong.
Your Dog Or Cat Has Stung By A Bee – Now What?!
Still, even if you take all the precautions, accidents happen. Pets can be stung on the face, inside the mouth, on their paws, or on other parts of their bodies if they snap at, sit on, or step on a bee. So it’s best to be prepared!
How To Tell If Your Pet Has Been Stung
If you don’t actually see your dog cat get stung by a bee you’ll need to look for other clues of the encounter. Check for swelling, pawing at the face, or obsessive licking. These are signs that your best friend has met business end of a stinger.
If you notice these symptoms, you’ll need to watch your pet carefully for the next few hours. Some animals, like some people, are highly sensitive to insect toxin. In those cases, your pet could experience Anaphylactic Shock, a severe allergic reaction which can cause the circulatory system to shut down.
Signs Of A Serious Allergic Reaction To A Bee Sting
If you notice any of the following symptoms, which usually occur within an hour of the sting, DO NOT DELAY in getting veterinary care:
1. Severe and profuse swelling (i.e. entire face as opposed to just the lip)
2. Difficulty breathing or increased respiratory effort possibly due to throat swelling
3. Very pale or blue-tinged mucous membranes (inner lips and gums)
4. Rapid and/or irregular pulse
5. Prolonged Capillary Refill Time (Refer to “Checking Your Pet’s Vital Signs,” but if gums are pale, or if it takes longer than 2 seconds for the color to return to the gum when pressed with your finger, your pet needs immediate medical care.)
Treating Your Pet’s Bee Sting
Even if your pet doesn’t appear to be having a severe reaction, the sting might still be painful. Keep a close on him while you gather the following items:
- Cold Pack
- Baking Soda or Meat Tenderizer Containing Papain
- Epi-pen, if your pet has had previous encounters with bees and is known to be allergic
- Water
- Syringe, Eye Dropper, or Spray Bottle
- Diphenhydramine/Benadryl®
(Note: The product you purchase should contain diphenhydramine as the only active ingredient. Some products contain additional ingredients such as xylitol (in Benadryl no-sugar syrups) or decongestants such as pseudoepinephrine. Both xylitol and pseudoepinephrine are potentially lethal to dogs. So check with your vet, and only consider giving Benadryl if it contains diphenhydramine and nothing else.)
Depending on where your dog or cat has been stung by bee, there are some steps you can take to help speed their recovery.
IF THE STING IS INSIDE THE MOUTH:
— Offer your pet an ice cube or small amount of ice water to minimize swelling
— Seek immediate advice from your veterinarian, as the mucous membranes of the mouth will more quickly absorb the insect toxin. Should your pet’s tongue swell, giving rescue breathing might be impossible, and a veterinarian will be best equipped to help.
IF THE STING IS ELSEWHERE ON THE BODY:
The stinger might be concealed in your pet’s fur, or it could already have been pawed away. But if you can see it, flick it away with a credit card, popsicle stick, or your finger nail. Do not pull the stinger with your fingers or tweezers as you can puncture the poison sac, allowing more toxin to enter your pet’s body.
If you have an epi-pen prescribed specifically for your pet due to previous allergic reactions, read and follow the attached instructions. Follow up immediately with your veterinarian as anaphylaxis can occur.
If you can locate the sting site, dab it with a paste made from 1 Tablespoon baking soda or meat tenderizer mixed with a drop of water. (Meat tenderizer and baking soda are both alkaline and work to counteract the acidity of the toxin. Also, the papain in tenderizers breaks down the protein in the toxin.)
Administer diphenhydramine (Benadryl® antihistamine). While this medication is generally considered safe for cats and dogs, consult with your veterinarian to determine the proper dosage. Also discuss any other medications your pet is taking and any pre-existing medical conditions. Diphenhydramine will help relieve mild allergic reactions and make your pet sleepy, allowing him to relax and prevent him from scratching the sting site. If swelling persists for more than 6-8 hours, consult your veterinarian for further treatment.
Apply a cold pack to reduce swelling, but remove every few minutes to avoid frostbite. Placing the cold pack in a damp washcloth will help keep your pet’s skin from getting too cold.
Homeopathic Tip: Apis Meliffica, also known as Honey Bee, can aid the body in reducing the burning or stinging pain.
Preparations For Traveling With Pets
Of course, bee stings don’t always happen when you’re at home. So make sure the items you’ll need to treat a bee sting are in the first aid kit in your car and in your hiking backpack.
Also, if your pet is too large to fit into your backpack, consider getting an emergency sling (affiliate link) that would allow you to carry him back to your car.
Being prepared allows you to give your pet the attention he needs quickly. And the sooner he’s better, the sooner you can both get back to having fun.
About the Author: Denise Fleck has trained with 12 national animal organizations and has taught more than 10,000 pet lovers animal life-saving skills. She’s developed courses, written nine books, and created a line of pet first aid kits and posters so people can help their pets BEFORE veterinary care can be reached.
THE BEST INFORMATION FOR PET FRIENDLY LODGINGS, RESTAURANTS, AND THINGS TO DO TOGETHER.
GoPetFriendly is the nation’s fastest-growing pet friendly travel planning platform, with more than 1 million trips booked every year. Their unique content provides loads of inspiration, and their best-in-class database provides all the information you need to plan a memorable pet friendly experience. With free web and mobile applications, GoPetFriendly is helping people and their pets do more together.ABOUT GOPETFRIENDLY
Angel Fund Helps Puppy Stricken by Parvovirus

Victoria Romero, a young graphic design student, had wanted a dog since she was eight or nine years old. When she turned 16 a couple of years ago, she suggested to her mother that she give her a dog instead of a Sweet Sixteen party.
Her mother said no. “So I had never had another opportunity [to have her own dog] until now,” she said. A friend of her Mom, who had a female Maltese-Poddle mix puppy, wanted to find someone who could take the dog off her hands.
Victoria took charge of Kona in mid-November. The dog was lethargic and she knew that the animal would need shots. “So I called the [Aliso Animal] hospital and made an appointment for the next day,” she said.
Dr. David Bahou examined the dog and told Victoria that her new pet had parvovirus. “This is my first dog and I really wanted to be careful with her,” she said. “I was crying the whole time in the hospital because I thought maybe I had done something wrong.” At the time, she had been Kona’s owner only a couple of days.
Dr. Bahou assured her that she was not at fault. “He said that Kona’s symptoms would have started five to seven days after exposure so she had gotten the virus when she was with the previous owner,” Victoria said.
But there was another issue: paying for Kona’s treatment.
“I was very sad because I did not have the money I needed,” Victoria said, “and the only option was putting her down. I did not want to do that. I was already so attached to her. I loved her so much that I couldn’t do that. I called my family and friends to invite them to give me a little bit each.
“Dr. Bahou and the hospital staff really wanted to help me,” she said. “When they told me about Angel Fund, I said let’s do that. I just didn’t want to see Kona get worse because she already was so lethargic.
“I’m really grateful for Angel Fund and what they did. It really helped me out. I hope other people can find out about Angel Fund.”
Victoria, a student at Laguna College of Art and Design, works as a baby sitter for her mother and in a child day care role at a local school district. She expects to graduate from her program in the spring of 2025.
She heads to one of the schools in the district each work-day morning to help young students who participate in a pre-school program, she said. “I work about an hour and a half,” she said, “getting their minds awake for school.” Then she returns home to supervise her two younger siblings while her mother works.
Her mother does house cleaning and some gardening work and manages a group of workers.
Kona who is now about five months old and weighs about three pounds, is doing well. “She’s now about 100 percent,” Victoria said. “She has been running around the house trying to steal our shoes.”

Veterinarians say fears about ‘mystery’ dog illness may be overblown. Here’s why
PUBLIC HEALTH
DECEMBER 1, 20235:00 AM ET
HEARD ON MORNING EDITION By Will StoneLISTEN· 3:46
Many dog owners are worried about reports of a mysterious respiratory illness affecting dogs.
I watched anxiously as my 80-pound doodle trotted off to his regularly scheduled doggy daycare, blissfully unaware that he’d soon be swapping all manner of germs with his buddies.
I wondered, does this constitute a high-risk situation? This was the same small circle of dogs he played with every week, but I had no clue where the others spent their time.
Would he come home with more than a healthy dose of slobber? Maybe, even, a new and poorly-understood pathogen?
Reports of respiratory illness afflicting dogs have put many dog owners like myself on edge in recent weeks.
Social media is filled with increasingly distressing headlines and anecdotes of otherwise healthy pets coming down with a raft of symptoms, everything from a hacking cough to sometimes life-threatening complications.
Most concerning, veterinarians say they’re unable to identify what’s making the dogs ill and the go-to treatments for canine respiratory illness, generally called “kennel cough,” appear to be ineffective.
The list of states with suspected cases of a “mystery illness” has grown to include most regions of the country.
The uncertainty is worrying for the 65 million households with a dog — especially those whose pets have fallen sick. In rare cases, dogs have died.
But veterinarians who study infectious diseases say this may, in fact, not be an outbreak of a singular illness at all. There’s still scant evidence connecting these cases with any common pathogen, let alone to an altogether new one.
“It’s entirely possible that there are just a ton of different bugs and viruses causing disease in different parts of the country,” says Dr. Jane Sykes, a professor at UC Davis School of Veterinary Medicine who focuses on infectious disease. “We just have to be a bit careful about panicking.”
Because the U.S. doesn’t have a robust surveillance system for infectious disease in dogs, it’s hard to track these cases and discern whether anecdotes and scraps of data add up to widespread and concerning patterns.
“Two things keep getting mixed up,” says Dr. Scott Weese, an infectious disease veterinarian at the Ontario Veterinary College. “Do we have more disease? And do we have something new? Because those are not necessarily connected.”
Poor clinical understanding of ‘atypical’ illness
Weese says it seems that certain parts of the country are experiencing an uptick in canine respiratory illness. However, it’s possible the deluge of media coverage and attention on social media has created the appearance of a nationwide outbreak that may not exist in reality.
“I get an email a couple of times a week saying, ‘hey, are we seeing more respiratory disease in dogs?” he says, “But I’ve been getting that email for like five years.”
Dogs often pick up viruses and bacteria from other pets when socializing or being cared for in group settings.
Despite all the attention on individual cases, there’s nothing at this point “that would indicate there’s a national outbreak, anything that would indicate these are all medically connected to each other,” says Dr. Silene St. Bernard, a regional medical director for VCA Animal Hospitals, which runs more than a thousand hospitals in the U.S. and Canada.
Of course, none of this skepticism rules out the possibility that there is a new pathogen starting to spread.
For example, researchers in New Hampshire have identified an odd bacteria that could be relevant, although they haven’t yet confirmed this is actually what’s causing illness in some dogs.
“The three choices are: There is not a new disease out there. There is a disease whose incidence is particularly high right now and it’s a known agent,” says Dr. Kurt Williams, who directs the Oregon Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, “Or there’s truly something new and novel out there.“
While there’s no official tally, there are now hundreds of cases of an “atypical canine respiratory disease,” according to state health officials and medical organizations in more than a dozen states.
However, Williams cautions this framing can give the impression that a clearly defined disease is spreading. “We have a very poor understanding of the cases clinically,” he says.
Generally speaking, the unifying symptom seems to be a persistent cough that doesn’t resolve as would be expected with typical cases of kennel cough. In the worst cases, dogs can come down with severe pneumonia, which sometimes develops rapidly.
Negative tests may not rule out known pathogens
Similar to veterinarians in other states, Dr. Melissa Beyer says she’s not seeing dogs with an unidentified illness dying in high numbers. What’s puzzling is they can’t identify the causes of their illness.
“We’ve been running respiratory panels to check about 20 different viruses and bacteria,” says Beyer, who runs South Des Moines Veterinary Center, “A lot of them are coming back negative.”
This observation by veterinarians around the country has raised the specter of a new pathogen, but there’s actually many reasons why the PCR tests used for canine respiratory illness could come back negative, says Sykes of UC Davis.
The sample collected could simply be too small, or taken from the wrong part of the body; the levels of the pathogen can change from day to day, or the dog’s body might have stopped shedding it by the time the sample was collected.
Even if it’s a well-known bug, the genetic sequence might be different enough that the PCR test fails to detect it.
“For some of these organisms, negative results are even more common than positive test results,” she says.
Sykes, who founded the International Society for Companion Animal Infectious Diseases, says the observations that dogs are resistant to standard treatment is thorny because many dogs are treated unnecessarily with antibiotics, when, in fact, they have a viral illness.
“What’s actually being said here by veterinarians in these different locations is really that dogs are taking a long time to recover,” she says.
Symptoms could be caused by a ‘pathogen soup’
Of the many possibilities, she suspects one could be a “pathogen soup,” essentially a mixture of co-occurring infections that are making dogs especially sick and prolonging their recovery.
Respiratory disease in dogs wax and wane and the last few years have seen more “dramatic swings” where outbreaks last longer and take place across broader areas, says Dr. Weese.
The epidemiology around this illness is especially hazy because there’s already some mix of the usual suspects, like Bordetella and canine respiratory coronavirus (not related to COVID-19), with outbreaks of canine flu layered on top of that.
The uptick in illness doesn’t happen in a vacuum, either: Dog ownership in the U.S has gone up steadily, vaccinations have been disrupted in recent years, and the holiday season has led more people to board their dogs or bring them on travel and mingle them with other pets.
Pathologist search for clues in the lab and in lungs
Still pathologists are keeping an open mind as they collect samples from sick dogs and search for clues.
“I do trust veterinarians,” Williams says, “If they say we are seeing increased numbers of cases and they’re behaving clinically differently than we’re used to, we need to pay attention.“
In New Hampshire, a team of researchers have used genetic sequencing to turn up evidence of what appears to be a new bacteria, similar to Mycoplasma.
While they haven’t been able to culture the bacteria, they’ve identified it in samples collected from dogs who fell ill in New Hampshire last year and from dogs in neighboring states this year.
“We think this may be a pathogen,” says David Needle, a pathologist at the New Hampshire Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, “We don’t think it itself is responsible for mortalities very often, but it may allow for secondary infections that could cause mortalities.”
Needle is analyzing samples from other states to see if they can find the same genetic material in sick dogs there.
While intriguing, Weese points out that Mycoplasma can commonly be found in dogs with and without respiratory disease. He says it’s way too soon to assume this is behind any of these outbreaks.
“We just don’t know at this point,” he says.
In Oregon, Williams is skeptical that would explain what he’s seeing in his state, saying it’s possible something distinct is happening in the Pacific Northwest.
In fact, he’s in the early stages of examining the lungs of dogs who died from the atypical respiratory illness that has sickened more than 200 dogs in Oregon. So far, he’s finding acute injury in the small air sacs, called alveoli, and bleeding from that into the lungs.
“I don’t want to get out over my skis here, but I’ve looked at a lot of dog lungs in my career, and these are a little bit different,” he says, “So it makes me think, maybe, there’s something out there.”
Sponsor Message
Take precautions but don’t succumb to fear
For now though, veterinarians tell NPR it’s wise for dog owners to take common-sense measures, like avoiding contact with sick dogs and making sure your dog is up to date on its vaccine.
Ultimately, Weese says it will depend on your situation.
“If there are a lot of sick dogs in your area, then it is reasonable to be more restrictive. If you’ve got a dog that’s at high risk for disease, be more restrictive,” he says.
Some people may want to steer clear of “high traffic” public places like dog parks and if possible, boarding facilities, groomers and other crowded settings, says Dr. Ashley Nichols, president of the Maryland Veterinary Medical Association.
“Those are the activities that if you’re nervous about exposure, I would avoid because that’s where dogs with many backgrounds, many immunization levels and things like that mix,” she says.
Nichols worries about the exponential rise in fear among some pet owners. She and her colleagues have noticed it’s led some to skip routine health care, worried their dog might catch something at the clinic.
“I understand people’s concerns. I think avoiding the vet clinic is not the way to go,” she says.
And if your pet does get sick, get them seen immediately. Ashley Dozier, a vet tech in Virginia Beach, initially wasn’t too worried when her young golden retriever started coughing earlier this fall. That changed as his condition deteriorated, though.
“I brought him in to work and he was diagnosed with pneumonia,” says Dozier. “He went a total of nine weeks on three different types of antibiotics and a round of about three to four weeks of steroids.”
Now off the steroids, she says he’s finally starting to bounce back.

